Biology Dept Kenyon College |
|
 |
Biology Dept Kenyon College |
|
 |
Cell division in Bacteria; in EukaryotesFor reproduction, all cells need to copy their chromosomes exactly and pass on an identical copy to each daughter cell. (Of course rare "mistakes" occur -- cells actually have evolved to favor rare mistakes. Why?)Two different mechanisms do this in cells: Bacterial cell fission, in which the circular chromosome is replicated. Eukaryotic cell cycle, including Mitosis, in which multiple linear chromosomes are separated and passed on. Bacterial Cell DivisionReplication of the chromosome starts at the origin attached to the cell wall, near the midpoint of the cell. Replication occurs bidirectionally around the chromosome, as the cell elongates. New replicating forks can start before the first cell division takes place; this phenomenon allows an extremely rapid rate of reproduction.
Image 69091JWA from Dennis
Kunkel Microscopy, Inc. DNA starts replication at the origin,
and two DNA polymerase complexes proceed in opposite directions.
Each complex (called a replisome)
contains two whole DNA polymerases (WHY?). Before the DNA circle has completed replication a second round of replication can begin. Thus two "generations" of DNA replication occur simultaeously. Can this ever happen in eukaryotes? Why or why not?
In eukaryotes, DNA replication actually occurs in S phase of interphase. Stages of interphase include:
The big problem with eukaryotes is that they have to replicate linear chromosomes with special ends called telomeres. To do this, they need to use a special enzyme called telomerase, actually related to the reverse transcriptase of HIV virus. Telomerase activity may play a crucial role in human aging; if the chromosome ends fail to replicate properly, the chromosomes gradually lose parts of their end sequence. For more information
on telomerase, go here.
Eukaryotic Cell Division--Mitosis
Click
on picture for stages:
Meiosis: Division to produce sex cells 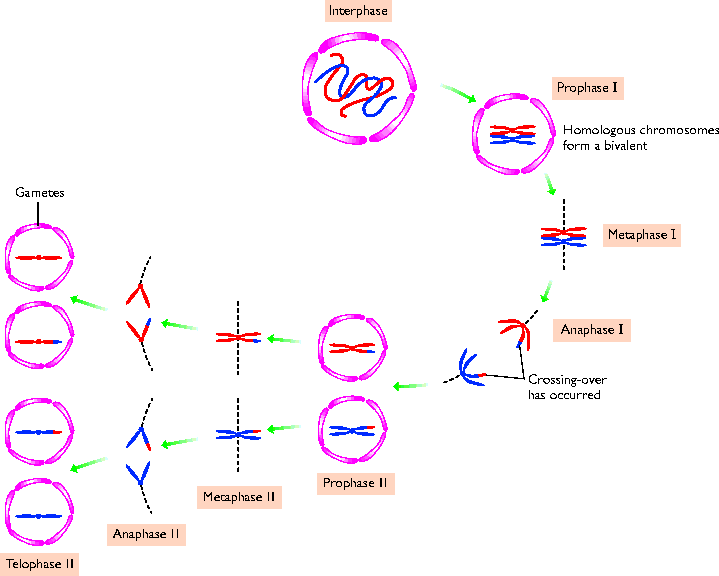
T. A. Brown, Genomes, BIOS What happens to chromosome copy number (ploidy) during DNA replication followed by mitosis or meiosis? Mitosis: 2N -> 4N -> 2N Meiosis: 2N -> 4N -> 2N -> 1N Problems: (1)
Bacteria can divide TWICE in the time it takes to complete replication
of
(2) Suppose that in a field of cells in tissue culture, about five percent of cells show the condensed chromosomes of mitosis. If the duration of mitosis is five minutes, what is the overall generation time of the cells? |