Potential Research Organisms/Systems
This is not intended as an exhaustive list of what is out there to work with but rather a list of things
that we have found works well in the past.
|
If you are interested in questions at the molecular level contact the appropriate instructor
to select a system.
|
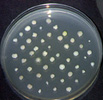  |
Yeast and Bacteria - can be used to study the effects of ultraviolet light, nutrition, antibiotic
resistance, pH tolerance and population growth |
|
|
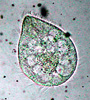
Protists - can be used to study predator prey associations, toxicology, cell function, locomotion. |
|
| Fungi and Cellular Slime Molds - can be used to explore a variety of developmental questions |
|

|
Lemna sp. can be used to look at questions related to toxicology, nutritional studies, competition
and population growth
Lumbriculus sp. an aquatic worm is also a good subject for toxicological, behavioral and regeneration
studies. |

|
|
| Arabidopsis - used for questions related to plant genetics, growth, and development. |
 |
Lettuce or Radish seeds are often used for studies involving chemical competition (allelopathy) between
plants. |
|
| Moss, Corn Embryos or Seed plants can be used to study the effects of various plant hormones, nutrients,
light, competition, herbicides, salt stress etc. on growth. |
 |
Alliaria petiolata - is an introduced invasive weed. Both field and lab studies can be done using
this plant. The chemical properties of this plant may alter the micorrhizal associations between forest plants
and their hosts, prevent herbivores from feeding on it, or inhibit the growth and germination of potential competitors. |
|
| Trees, Shrubs, Vines can be used for field studies related to species diversity and richness as well as
questions related to the impact of deer on forest regeneration. |
 |
Daphnia sp. can be used as the prey for a variety of foraging studies. They also respond to
chemical cues from fish and can be used for toxicological studies. |
|
| Planaria - a type of aquatic flatworm used for studies involving regeneration, chemical cues, and neurobiology. |
 |
Crayfish and/or Snails make good subjects for behavioral and foraging theory studies. Crayfish can
also be used in a variety of physiological studies. Field studies on both groups are also feasible. |
|
 |
Isopods - these organisms can be used in a variety of behavioral studies. Field studies on distribution
are also possible. |
|
 |
Chickadees and other birds make good subjects for food choice, habitat use, vigilance and foraging studies.
Chicken eggs can be used for studies of nest predation. |
|
 |
Ants - are good subjects for studies on foraging behavior and food choice. Good for lab or field projects |
|
 |
Uca pugilator are good subjects for a wide variety of physiological and behavioral studies. |
|
 |
Soil and stream invertebrates can be used in studies on species diversity and the impact of different
environmental conditions on these organisms. In streams they provide an index of water quality. This type of study
has both field and lab components. |
 |
|
 |
Amphibian tadpoles can be used for a variety of developmental projects. They can also be used to explore
predator avoidance and response to chemical cues from fish or dragonflies. Growth studies are also possible |
|
 |
Global Information System technology can be used for a variety of field projects. Here it is use to map the distribution
of 13-lined ground squirrel nests. It can be useful in a wide variety of field studies. |
|
 |
Manduca sexta can be used for behavioral |

|
physiological, developmental or neurological studies.
|
 |
|



















